Internet: One thing everyone is aware of and for some people It is also difficult to live without it. From Social media to Movies to Youtube everything is the Internet.
Now, let’s learn how it works?
The Internet is delivered in two ways 1.Satellites 2.Undersea Cables Or Submarines.
Data is simply facts and statistics collected together for reference or analysis. Let’s see how this data is stored on the Internet First:
Let’s take an example of an Image or Video. When we upload a picture or video. The data is stored in the data centers which contain Servers.
The created data will be stored with an address called as IP address(Ex:255.255.255.0) Every Domain or a website will have an IP address (Ex:172.217.11.174 Google .com)
When a user’s like you and me search on the web. A request is sent to the servers present in the data centers in different locations around the world.
These data centers accept the requests and send back the information asked back to the user using satellites or submarine cables.
Data transfer via satellite is not a viable option because the signals should be passed two ways and also have a lot of disturbances like bad weather, Slow transfer rate, etc.
Submarine cables came to existence because of these issues.
A Submarine cable is laid on the sea bed between land-based stations to carry telecommunications signals across stretches of the ocean throughout the globe.
This is a fiber optic cable and data is passed between them through the form of light from one end to another end.
These cables are loaded and taken into the ocean on a vessel, Connecting the data centers. A special underwater is dropped into the ocean which lays the cables
and later is inspected by a technician.

Providing the Internet to end user involves a three step cycle and three tiers involved
Tier 1:This comprises of a wide network of submarine cables, spread across the globe connected with the data centers. Some of the owners of Sea-cables are At&T, Verizon, Google, Tata, Telia Etc.
Tier 2:This is responsible to connect with Tier 1 and Tier 3. They purchase the data from tier 1 who owns a connection with the data centers via sub-sea cables.
Few of the owners are reliance. Airtel, China Telecom, Tata’s TGN-IA.
Tier 3:Local Internet service providers like airtel Fibernet, Act Fibernet, Hathway, BSNL Etc. They purchase data from tier 2 and provide services to households.
Thus, When a user requests certain data through a phone or laptop, the first request goes to the local ISP from a user, then to the tier 2 provider and tier 1 provider.
It reaches to the data center.
Data center’s process the requested information and send them back the user’s through the same channel.
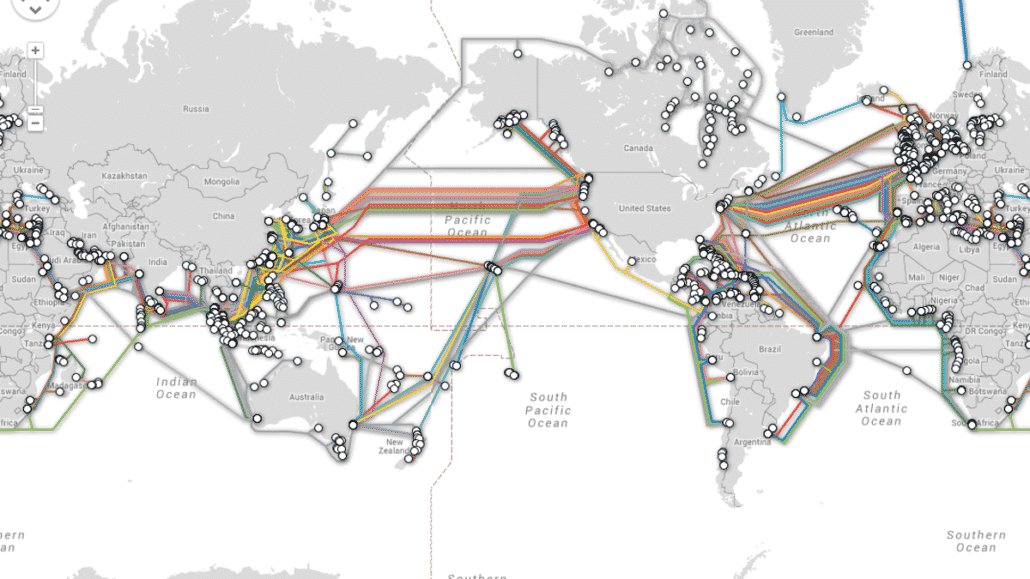
In India, there are 9 cable landing points including Mumbai, Chennai, Cochin, Puducherry, Tuticorin, etc.
Recently, PM Modi has launched cable connectivity to Andaman & Nicobar islands dedicated to the nation and Lakshadweep will be connected in the next three years.
This helps people of islands for better connectivity to Internet. Now,You know how the internet works.
Also Read :

